99. Recover Binary Search Tree
Tree Depth-First Search Binary Search Tree Binary Tree
Problem - Recover Binary Search Tree
Medium
You are given the root of a binary search tree (BST), where the values of exactly two nodes of the tree were swapped by mistake. Recover the tree without changing its structure.
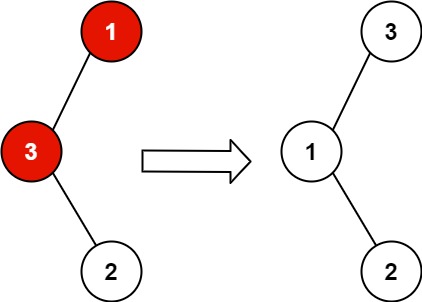
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,3,null,null,2] Output: [3,1,null,null,2] Explanation: 3 cannot be a left child of 1 because 3 > 1. Swapping 1 and 3 makes the BST valid.
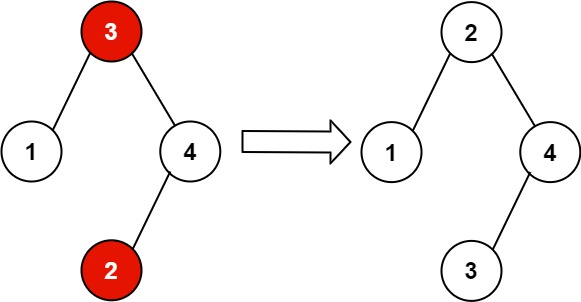
Example 2:
Input: root = [3,1,4,null,null,2] Output: [2,1,4,null,null,3] Explanation: 2 cannot be in the right subtree of 3 because 2 < 3. Swapping 2 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 1000]. -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
Follow up: A solution using O(n) space is pretty straight-forward. Could you devise a constant O(1) space solution?
Solutions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | |
Submission Stats:
- Runtime: 4 ms (44.52%)
- Memory: 18.1 MB (76.47%)