94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
Stack Tree Depth-First Search Binary Tree
Problem - Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
Easy
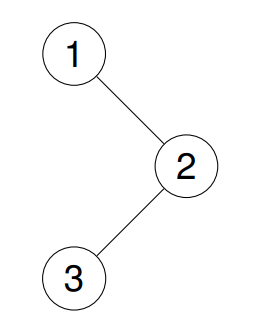
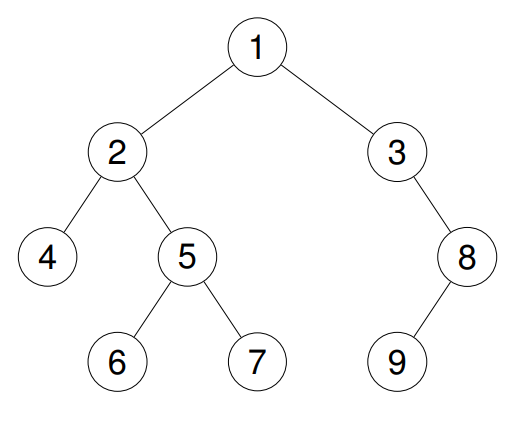
Given the root of a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Example 1:
Example 2:
Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 4:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
Solutions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | |
Submission Stats:
- Runtime: 0 ms (100.00%)
- Memory: 17.7 MB (84.31%)