896. Smallest Subtree With All The Deepest Nodes
Hash Table Tree Depth-First Search Breadth-First Search Binary Tree
Problem - Smallest Subtree With All The Deepest Nodes
Medium
Given the root of a binary tree, the depth of each node is the shortest distance to the root.
Return the smallest subtree such that it contains all the deepest nodes in the original tree.
A node is called the deepest if it has the largest depth possible among any node in the entire tree.
The subtree of a node is a tree consisting of that node, plus the set of all descendants of that node.
Example 1:
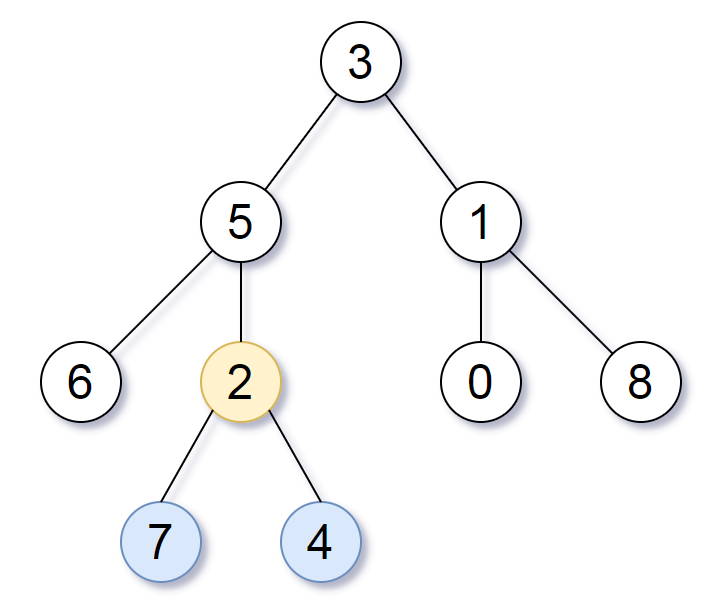
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4] Output: [2,7,4] Explanation: We return the node with value 2, colored in yellow in the diagram. The nodes coloured in blue are the deepest nodes of the tree. Notice that nodes 5, 3 and 2 contain the deepest nodes in the tree but node 2 is the smallest subtree among them, so we return it.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: [1] Explanation: The root is the deepest node in the tree.
Example 3:
Input: root = [0,1,3,null,2] Output: [2] Explanation: The deepest node in the tree is 2, the valid subtrees are the subtrees of nodes 2, 1 and 0 but the subtree of node 2 is the smallest.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[1, 500]. 0 <= Node.val <= 500- The values of the nodes in the tree are unique.
Note: This question is the same as 1123: https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-deepest-leaves/
Solutions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | |
Submission Stats:
- Runtime: 0 ms (100.00%)
- Memory: 19.6 MB (11.50%)