1465. Maximum Product Of Splitted Binary Tree
Tree Depth-First Search Binary Tree
Problem - Maximum Product Of Splitted Binary Tree
Medium
Given the root of a binary tree, split the binary tree into two subtrees by removing one edge such that the product of the sums of the subtrees is maximized.
Return the maximum product of the sums of the two subtrees. Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Note that you need to maximize the answer before taking the mod and not after taking it.
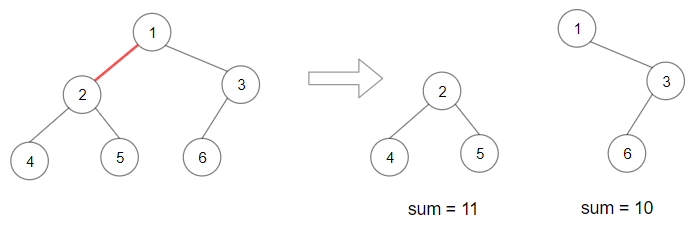
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6] Output: 110 Explanation: Remove the red edge and get 2 binary trees with sum 11 and 10. Their product is 110 (11*10)
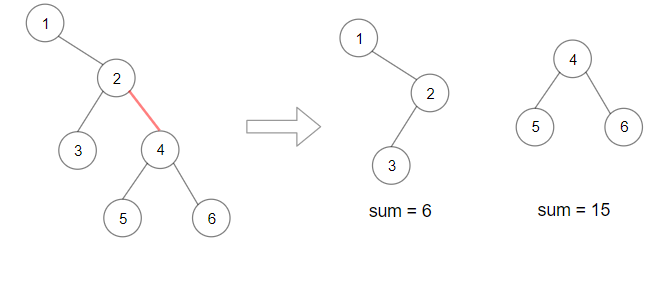
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,null,null,5,6] Output: 90 Explanation: Remove the red edge and get 2 binary trees with sum 15 and 6.Their product is 90 (15*6)
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 5 * 104]. 1 <= Node.val <= 104
Solutions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | |
Submission Stats:
- Runtime: 48 ms (80.99%)
- Memory: 46.5 MB (5.32%)